Knowing your way around a debug source and knowing how to set and remove breakpoints is very important, but sometimes you need more than that. That’s where watch conditions come into play.
You use a watch condition to monitor whether the current value of an expression or a variable changes while your program runs. Setting watch conditions is similar to setting conditional breakpoints, with one important difference: Watch conditions stop the execution of the program as soon as the value of a watched expression or variable changes from its current value, regardless of the place in the code where that change occurs. Conditional breakpoints, on the other hand, stop the program only if the variable has the value specified in the breakpoint condition when the execution reaches the line where the breakpoint was set. In other words, a watch condition monitors the value of the variable globally, while the breakpoint simply checks whether a certain condition is met before the execution of a given line of code.
The watch condition monitors a variable through the content of a storage address, computed at the time the watch condition is set. When the content at the storage address is changed from the value it had when the watch condition was set, the program stops. The same thing occurs when you tell the debugger to continue the execution (I’ll explain this later), and the value of the watched variable changes again. To put it in another way, once you put a watch on a variable, whenever that variable’s content changes, the program stops, relinquishing control back to you.
There are a few more important facts you need to be aware of when it comes to watches:
- Watches are monitored systemwide; a maximum of 256 watches can be active simultaneously. This number includes watches set by the system, which are invisible to you. Depending on the overall system use, you might be limited in the number of watch conditions you can set at a given time. If you try to set a watch condition while the maximum number of active watches across the system is exceeded, you receive an error message, and the watch condition is not set. Personally, I’ve never seen this happen, but IBM says it’s possible.
- Unlike breakpoints, watch conditions can be set only when a program is stopped under debug and the variable to be watched is in scope. When you try to add a watch before the program execution begins, an error message is issued when a watch is requested, indicating that the corresponding call stack entry does not exist.
- After the command is successfully run, your program is stopped if a program in your session changes the contents of the watched storage location, and the Display Module Source screen is shown. If the program has debug data and a source text view is available (i.e., if it was compiled with a dbgview keyword other than *none and *stmt), it will be shown, popping up “magically.” The source line of the statement that was about to be run and would change the contents of the watched variable is highlighted. A message indicates which watch condition was met. Unfortunately, if the program cannot be debugged, the text area of the display will be blank.
- Eligible programs are automatically added to the debug session if they cause the watch-stop condition, which is a tremendous help when you have a complex service program structure.
- When multiple watch conditions are triggered on the same program statement, only the first one will be reported.
- You can also set watch conditions when you are using service jobs for debugging (that’s when you debug one job from another job). Typically, this is used to debug batch jobs, as explained later in this subseries.
Having said all of that, it’s time to show how to add and remove watches. As with breakpoints, there’s more than one way to do it. Let’s start with the debug command: Simply type watch <variable name> followed by Enter, and a watch will be set for that variable, saving the current content of <variable name> for later comparison. You can also position the cursor on top of the variable you want to watch (in the Display Module screen) and press F17.
When it comes to removing watches, you can press F18 in the Display Module screen or type WATCH and press Enter. Note that I didn’t specify any parameters. Either course of action will cause the Work with Watch window to pop up. In this window, similar to the Work with Module Breakpoints window, you can use option 4 to remove a watch. Finally, the CLEAR debug command can also be used for watches; simply type CLEAR WATCH <watch number> to remove a given watch. (Watch numbers can be obtained in the Work with Watches window.)
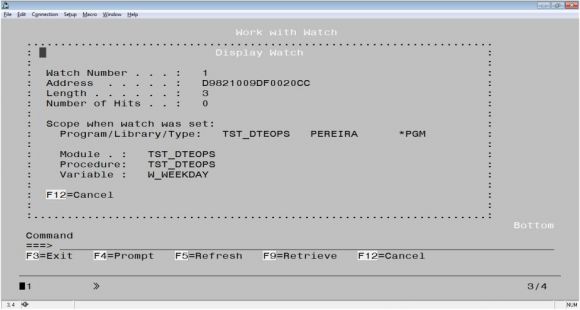
You’re probably wondering if you couldn’t simply use CLEAR PGM to nuke breakpoints and watches at the same time. The very smart people at IBM decided (wisely, if you ask me) that this would be a very bad idea, so you need to use CLEAR WATCH ALL instead to remove all the debug session’s watches. Note that it’s also possible to display details about a watch in the Work with Watches window by using option 5. Something similar to Figure 1 will be displayed.
Figure 1: Watch-related information, obtained via option 5 of the Work with Watch window.
This is nearly all the theory you need to know about the ILE debugger. The next logical step, which we’ll begin exploring in next month’s TechTip, is to start working with the real thing. For now, feel free to comment, suggest, or share your experience in the Comments section below or in the LinkedIn groups where my articles usually pop up.

















 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online