The LISTAGG function makes combining row values easier.
Several years have passed since I wrote articles on how to use the Db2 for i Connect By and Recursive Common Table Expression features to combine multiple row values into a single row. The following table represents the type of report that could be generated using the SQL detailed in those articles.
|
Make |
Models |
|
Chevy |
Malibu, Tahoe |
|
Ford |
Focus, Fusion, Taurus |
|
Honda |
Odyssey |
Both of these features depend on recursive SQL processing, which results in SQL statements that are difficult to understand. I believe that you will agree with this assessment if you go back and review the SQL examples in my earlier articles.
Luckily, the SQL standard has evolved since that time. Starting with the Db2 for i 7.2 release, the ability to combine multiple row values into a single row is much easier with the LISTAGG function. This simple SELECT statement can generate the make and model report shared earlier with the LISTAGG function.
SELECT make,
LISTAGG(model, ', ' ) WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY model) Models
FROM inventory
GROUP BY make
The LISTAGG function aggregates a set of string values for the current SQL group into a single string value. In this SELECT statement, the specified SQL group is defined by the values in the Make column. The LISTAGG function is executed for each unique value in the column. Based on this sample data for the inventory table, the LISTAGG function would be performed for three different groups: Ford, Chevy, Honda.
|
Make |
Model |
|
Ford |
Fusion |
|
Chevy |
Tahoe |
|
Honda |
Odyssey |
|
Ford |
Taurus |
|
Ford |
Focus |
|
Chevy |
Malibu |
The first argument on the LISTAGG function specifies that the model column will supply the set of string values that will be combined into a single string value. The second value on the LISTAGG function is the separator argument. In this instance, a separator value of ', ' has been specified so that string will be placed between each pair of model values returned for the current make. The separator argument is optional. If that parameter were dropped from this example, the Model value for Chevy would be 'MalibuTahoe'. The WITHIN GROUP clause is also optional. This clause is used to specify the order in which the individual string values are combined into a single string. If the clause is not specified, then Db2 can aggregate the string values in any order. In this example, the value will be sorted by the Model column value.
The LISTAGG function also supports additional options that can be useful, depending on the amount and type of data values being processed. The following query uses the LISTAGG function on the SYSCOLUMNS catalog view to generate the list of data types and column names using that type in the QSYS2 schema.
SELECT data_type,
LISTAGG(column_name, ', ')
WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY column_name) "Column Name List"
FROM qsys2.syscolumns WHERE table_schema='QSYS2'
GROUP BY data_type
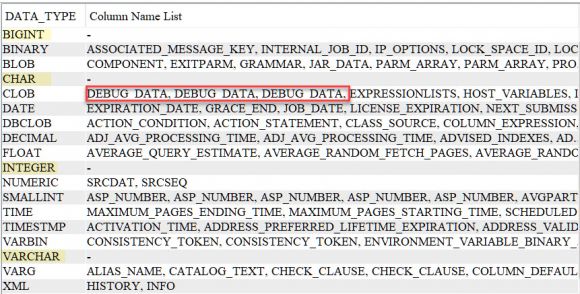
Figure 1 contains the output from the query. Notice in the Column Name List value for the CLOB data type that the DEBUG_DATA column name is repeated three times. The LISTAGG function includes duplicate values by default, but there is an option to change that behavior. It should also be obvious in this query output that the Column Name List is missing for the highlighted data type values (e.g., CHAR). That’s because a mapping error occurred due to the maximum size limit for the LISTAGG output string being exceeded. When the input string argument to the LISTAGG function is a VARCHAR column like column_name, the output size is 4000 or size of the input argument. In this example, column_name is a VARCHAR(128), so the maximum output size is 4000 bytes. Since there are so many columns in the QSYS2 schema defined with the highlighted data type values, a mapping error is returned for the LISTAGG function.
Figure 1: LISTAGG Query Output from SYSCOLUMNS
Below you’ll see that the previous query has been updated with new options to address the duplicate data and the mapping errors.
SELECT data_type,
LISTAGG(DISTINCT column_name, ', ' ON OVERFLOW TRUNCATE WITH COUNT)
WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY column_name) "Column Name List"
FROM qsys2.syscolumns WHERE table_schema='QSYS2'
GROUP BY data_type
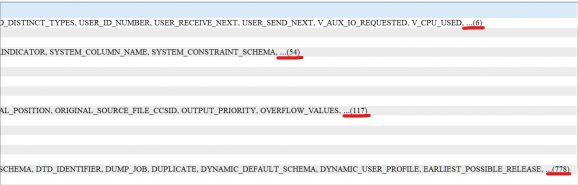
In Figure 2, the duplicate values in the LISTAGG output have been eliminated by simply adding the DISTINCT clause to the column_name input value. The data mapping errors also are no longer part of the query output thanks to the OVERFLOW clause. The default clause is ON OVERFLOW ERROR, which is the behavior shown in Figure 1.
The ON OVERFLOW TRUNCATE WITH COUNT option avoids the mapping error by truncating the string and adding a count of number of input values that were not added to the input string. This count of the truncated input values is shown in Figure 2. Another way to avoid the mapping error is to CAST the input column size to a bigger value (e.g., LISTAGG(DISTINCT CAST(column_name as VARCHAR(6000))…) to increase the LISTAGG maximum output size.
Figure 2: Query Output with Truncated Count Values
Surely, you now see how the LISTAGG function enables you to more easily combine values from multiple rows than the previous SQL support.













 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online