This article moves past the basics of data queues to the practical application of these lightweight communication marvels.
In previous articles on data queues and on keyed data queues, I presented the basics of how to create them and how to program for them. I went into some detail about the commands used to manage data queues and the RPG code required to access them. In these next articles, I'm going to go a slightly different direction and present you with the actual business case for using data queues in a robust multi-user (and even multi-platform) architecture.
First, a Conceptual Overview
Queues can be used to perform a number of functions. For example, queues serve as a way for a process on one platform to communicate with a process on another platform, regardless of whether the two processes are running at the same time. They can act as a buffer, allowing a faster process to send data to a slower process without having to wait. Or they can be used in one of my favorite roles, that of acting as a pipeline between different programming languages, specifically RPG and Java.
"Wait," you say, "ILE allows any languages to talk to one another!" And you are correct; the Integrated Language Environment (ILE) of the IBM i does allow any languages to directly call one another, passing parameters and effortlessly crossing the language barrier. But that integration isn't entirely uniform, and in fact in one case it's somewhat awkward and inefficient. Specifically, I'm talking about calling Java from RPG. While you can indeed call a Java class directly from an RPG program, it isn't exactly simple and it most definitely isn't efficient. The inefficiency arises from the nature of Java as a virtual machine; Java doesn't compile to machine code that is executed by the hardware; it's converted to bytecode that must run within a virtual machine. IBM has done a wonderful job of making that interaction as seamless as possible, but the implementation still requires any job that invokes RPG to have its very own JVM. Thus, a machine that has 100 users running an RPG program that calls Java has 100 JVMs. There are some other technical issues that together lead to an inexorable conclusion: the best way to use Java from an RPG program is through a Java server.
Java Servers and Data Queues
So that brings us to the actual implementation of a data queue architecture. Let's start with a simple picture. This image shows you the way a single data queue acts as the conduit between a Java server application and as many RPG clients as you need.
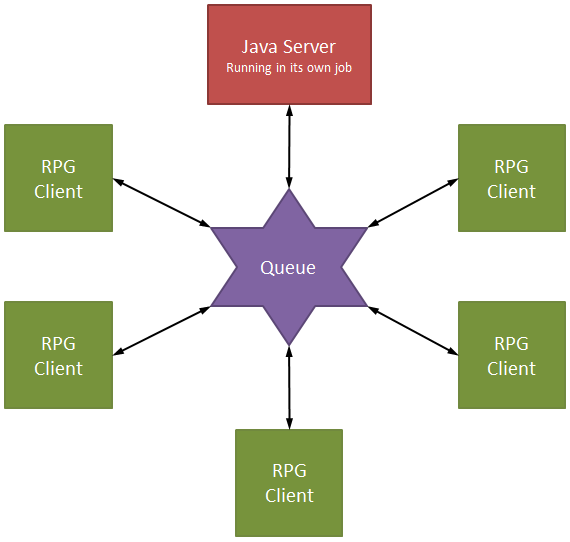
Figure 1: Here, the data queue is the conduit between one Java server application and multiple RPG clients.
Each of the RPG clients communicates only with the data queue, which is serviced by the Java server application. This is a keyed data queue, and the key is very simple: an ID representing the receiver. In a practical environment, I use a six-character ID field that is either a hard-coded value that represents the server or the six-digit job number of the client. Note that theoretically this would allow me to do this:
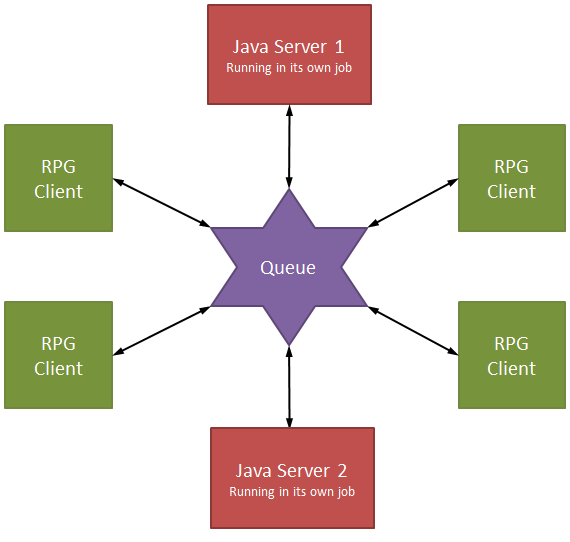
Figure 2: Alternatively, you could have multiple Java server applications.
I could have multiple Java servers, each with its own six-character ID value. Each RPG client could request a service from either server simply by putting an entry on the queue with the key of the desired server. What would the request look like? Something like this:
Key Value
Server ID
Client Job Number
Request ID
Data
Application-specific Request
The entry would be placed on the queue using the Server ID as the key. The appropriate server, in this case Java Server 1 or Java Server 2, would pop the entry and process the request. The response would then be placed on the same queue, except this time with the client job number as the key:
Key Value
Server ID
Client Job Number
Request ID
Data
Application-specific Response
Note that the two messages are exactly identical. The varying part, of course, is the application-specific data. The message to the server would contain the parameters for the request, while the response message sent back to the client would contain the results. Note that I haven't specified the size of the message; that's because it's very application-dependent. Some applications have messages that vary very little from one request to another, so it's relatively easy to identify the optimal size of the message. Others don't have the luxury of consistency, so you have to be a little more creative in how you design your infrastructure.
Practical Application
A design like this has practical application whenever Java is a better vehicle for a service function than RPG is. I've seen many example of it over the years, although I find two scenarios occur with some frequency.
First is the situation in which an entire Java library is used for a business function, typically some kind of open-source package like JasperReports. JasperReports is a fantastically powerful reporting package that allows you to generate PDFs, Excel spreadsheets, and all sorts of other documents programmatically from SQL databases, XML documents, and all sorts of other inputs. The package is so robust that you simply can't reprogram it in RPG, and the Java interface is dead simple to use. Stick the JasperReports interface into a server and your RPG programs leap from spooled files to multi-media juggernauts.
A second situation is when you have some sort of tool that generates Java code that you then need to use in a business environment. One typical environment is web services. Several tools exist that will take a standard Web Services Definition Language (WSDL) document and generate code to easily access that web service. However, the most standard of the tools tend to generate Java code and wrapping that Java code or otherwise altering it to efficiently interface directly to RPG would be difficult at best. Instead, the best approach is to put the generated code into a server and communicate between the Java and RPG via data queue.
Web services, of course, bring us back to the issue of data length. While many services provide a simple limited-length request/response interface, others are used to retrieve arbitrary lists of data. Those services require an infrastructure a bit more robust than the single-queued approach here, and in the next installment of this series I'll show you how to add a second queue to support any arbitrary amount of data. Until then, start thinking about situations in which you might want to invoke a Java function from your RPG code and use this article as a foundation for that design.
















 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online