IBM introduced pointers to many AS/400 programmers in RPG IV. Pointers generally have been the domain of those working in C or assembly language (among others), and they are not well understood by most AS/400 developers. RPG may have survived without pointers for years, but there are situations in which pointers are extremely useful. They are worth understanding.
Early RPG pointer support basically allowed you to set a pointer to the address of a field. To manipulate pointers, you had to resort to defining large, single-character arrays and getting the address of array elements using the %ADDR function. This “trickery” tended to obscure the simplicity of pointers. With V3R7, IBM has provided pointer arithmetic. This not only makes pointers a lot easier to understand, but it also makes them more useful and easier to use.
This article provides an explanation of pointers and what it means to base a data structure on a pointer. Then, it demonstrates the simplicity and effectiveness of pointer use in a program that retrieves the names of the jobs that are using an object.
A Pointer Primer
A pointer is simply a variable that is capable of containing an address that “points” to a memory location. Any data structure or field based on the pointer maps the area of memory that begins where the pointer points. By manipulating the contents of the pointer, you can use the same names to look at different areas of memory. (Each variable in memory, pointer or otherwise, starts at an address and continues for one or more bytes, depending on the data type. What is in those bytes makes up the contents of that variable.) What is actually in the pointer and how it is represented externally may be interesting but is generally not relevant to understanding pointers.
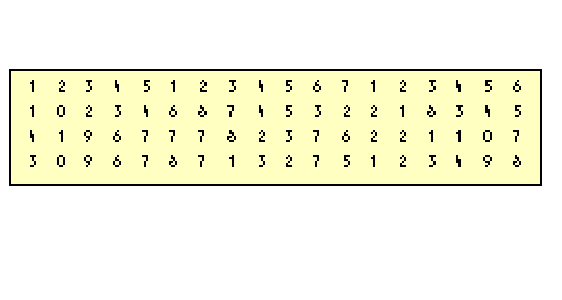
Let’s suppose you have a printed list of numbers representing customer information. The first five digits are the customer number, the next seven digits are the order number, and the six digits after that are quantity. (This is a poorly designed system,
but it is entirely hypothetical, so please bear with me.) A few lines might look like Figure
1.
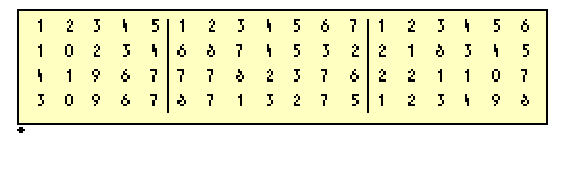
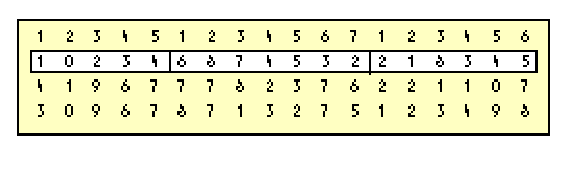
To accurately split up this information, you’d probably take a pencil and draw vertical lines after the 5th and 12th digits so you can easily and reliably tell customer number from order number from quantity, as shown in Figure 2.
Alternatively, you could create a clear plastic template like the one in Figure 3. By aligning the left edge and sliding it from row to row, you could now look through the template and distinguish customer number from order number from quantity. By itself, the template doesn’t tell you anything about the data. It’s only when you position the template on the page that it becomes useful.
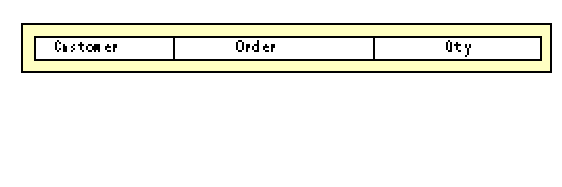
You can do the same thing with items in memory, using a data structure based on a pointer. Think of the data structure as a clear plastic template marked with boxes as in Figure 3, but where each box also has a name, as in Figure 4.
When you use the name in your program, you refer to whatever is showing through the box with that name.
Just as a plastic template is useless until positioned on the page, a based data structure is of no use until you put something in the pointer it is based on. Think of the pointer as defining the left edge, or base, of the template.
If the above list was in memory, you’d lay, or base, the left edge of the template at the first entry by setting the pointer to the address of the first item in the list, conceptually like Figure 5.
Since the template is really a data structure, you can now use the field names in the data structure to reference the data in the first list item by name. When you reference the field named Cust, you get the value 12345; reference Order and you get value 1234567; reference Qty and you get 123456.
Each entry is 18 characters long. Adding 18 to the pointer brings the base (left edge) of the data structure (template) to the next list item. You can reference the fields in it. Now, when you reference field Order, you get value 6874532, as shown in Figure 6.
This may sound a bit like a multiple occurrence data structure. It is. But using a pointer means there is no practical restriction on the number of occurrences. And it can adjust to changing data structure lengths without recompiling (see the “Dynamic Adjustment” sidebar). When you think of based data structures and pointers in terms of a clear plastic template that is being moved around, a lot of the mystery of pointers and based variables vanishes.
Hopefully, you don’t have any systems like the hypothetical list above. But many OS/400 APIs return data in similar long lists. Pointers, based data structures, and pointer arithmetic are the ideal ways to access this information. This leads into some surprisingly simple sample code.
A Practical Example Using Pointers
When one of our shop’s nightly processes needed exclusive use of an object and failed to obtain a lock, we needed to show the computer operator which other jobs were using the object. Older programs instructed the operator to interactively use the Work with Object Locks (WRKOBJLCK) command to resolve the conflict, but this wasn’t always followed, with occasionally unfortunate results. The WRKOBJLCK command does not produce an outfile, so we either had to resort to reading a spooled file (ugh!) or using an API to find which jobs had locks on the object. We chose to use the API, and the Get Object Users (GETOBJUSR) command was created.
The command returns a message string that might look like this:
M V P S D B / M V P S P R T P * F I L E i s i n u s e b y A S A P P O L L C C / J O B O P R / 7 4 1 4 5 6 ,
C D 5 4 D S P 1 C / S M I T H $ J / 7 4 2 3 7 5 , C D 5 4 D S P 2 9 / W H 1 M A M / 7 4 3 1 4 6 ,
C D 5 4 D S P 2 9 / W H 1 M A M / 7 4 3 1 5 7 p l u s 8 9 m o r e .
You can include this information in a message to the operator. It is an aid in determining the extent of the contention problem. This might prevent a late-night wake-up call. Up to the first four jobs are listed in full, and additional jobs are simply counted. Four was an arbitrary choice that will probably cover most nighttime contention problems, but the number of jobs is easily changed in the code. GETOBJUSR will also optionally return a file of jobs using the object. This file could be used to send messages to interactive users, asking them to free up the object in question or to sign off and go home.
A List API Overview
As has been covered in other articles, list APIs return information in a user space. The first part of the data returned to a user space is a header that is followed by a variable number of list entries, usually all of the same length. The length of the list entry is returned in the header, as is the offset from the start of the header to where the entries begin. This is a flexible design that allows IBM to change the length of the header or the length of each entry in future releases of the operating system yet not impact existing programs that call the API.
To use a list API, follow this conceptual outline:
1. Define a data structure to describe the user space header.
2. Base the user space header on a pointer.
3. Create the user space.
4. Load the user space header pointer with the address of the user space.
5. Define a data structure to describe each list entry.
6. Base the list entry data structure on a pointer.
7. Call the API to populate the user space.
8. Load the list entry data structure pointer with the address of the user space plus the offset to the first list element.
9. Process the first entry using names from the data structure.
10. Add the entry length to the pointer, if there are more entries.
11. Process that entry and repeat until there are no more entries.
How GETOBJUSR Uses Pointers and Pointer Arithmetic
The GETOBJUSR command and programs illustrate the above process. GETOBJUC is the CL command processing program (CPP) for GETOBJUSR and is not particularly noteworthy. It calls RPG IV program GETOBJUR, which does the work.
This section traces the implementation of the above conceptual outline in GETOBJUR. Since the outline is conceptual, the code isn’t necessarily in the same sequence as the points.
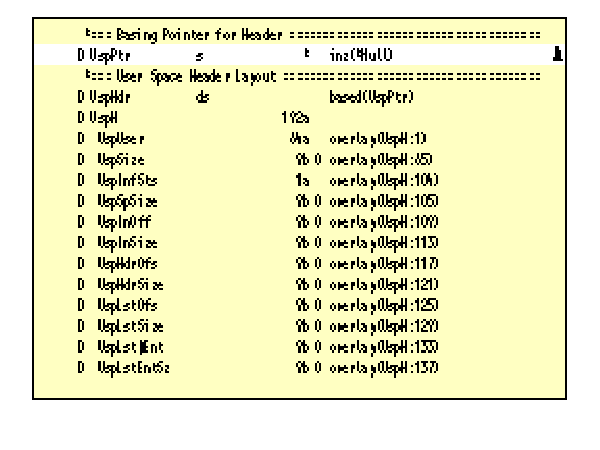
1. Define a data structure to describe the user space header. Copy member USPHDR (see Figure 7) defines data structure UspHdr, which describes the common header all the list APIs put at the beginning of the user space. It is used with other APIs, so it is a separate copy member.
2. Base the user space header on a pointer. USPHDR includes a pointer, UspPtr, and data structure UspHdr is based on UspPtr. UspPtr is initially defined as *NULL to clarify that it must be initialized before use (see Label A of Figure 7).
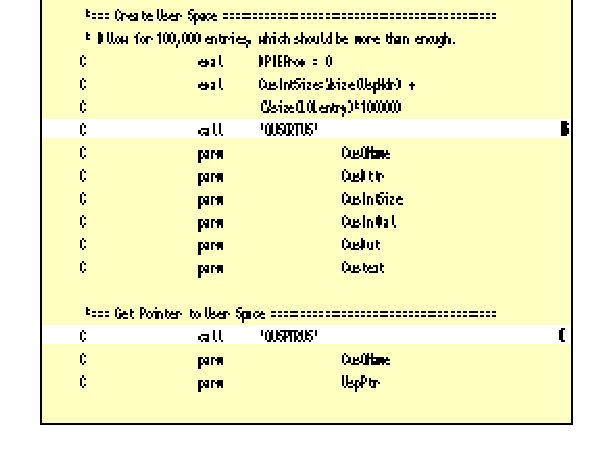
3. Create the user space. In the *INZSR subroutine, the user space is created by calling the QUSCRTUS API (see Label B of Figure 8).
4. Load the user space header pointer with the address of the user space. Immediately after the user space is created, a call to the QUSPTRUS API returns the
address of the user space into UspPtr (see Label C of Figure 8). Now, all the fields in the UspHdr data structure can be used, but they are still unpopulated.
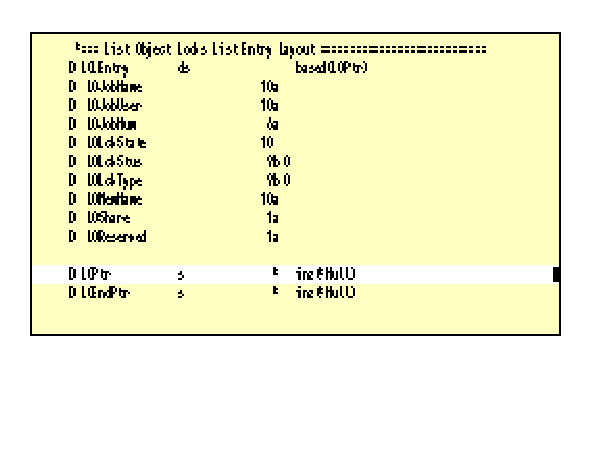
5. Define a data structure to describe each list entry. Information similar to that displayed by the WRKOBJLCK command can be returned by the QWCLOBJL API. Two list layouts can be returned by this API. OBJL0100, the one we are asking for here, is defined in the List Object Locks Entry (LOLEntry) data structure (see Figure 9).
6. Base the list entry data structure on a pointer. LOLEntry is based on pointer LOPtr (Figure 9, Label D).
7. Call the API to populate the user space. After a little housekeeping on the input parameters, the QWCLOBJL API is called to populate the user space. (This code is not shown.) A job can have more than one lock on an object. There will be one list entry for each lock. This program just wants to identify each job once. Therefore, you have to process the list entries in job name, job user, job number sequence and ignore all but the first of each group. (The list entries come grouped correctly. The API documentation makes no guarantee that it will always be this way, but it seems unlikely that it will change.)
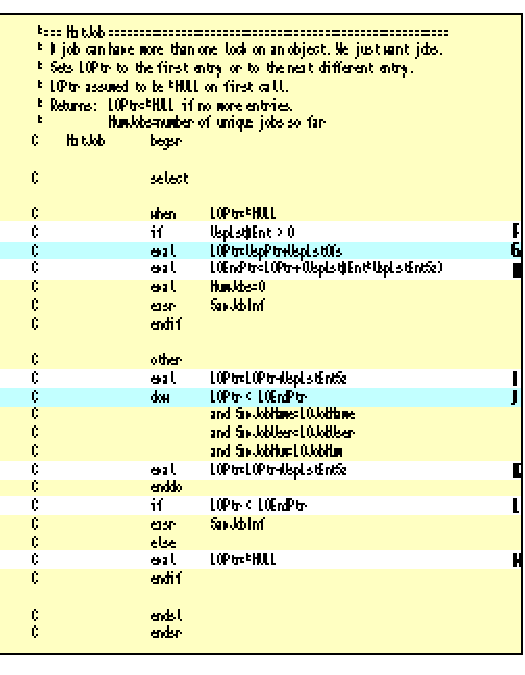
8. Load the list entry data structure pointer with the address of the user space plus the offset of the first list element. The main program loop is primed by calling subroutine NxtJob to set LOPtr to the address of the next unique job name, job user, job number combination (Figure 10, Label E).
If NxtJob (see Figure 11) finds that LOPtr is null, as it is since this is the first time through, LOPtr needs to be initialized to point to the first list entry. Since object locks may already have been cleared, NxtJob checks that at least one list entry was returned. (This is shown in Label F of Figure 11; UspLst#Ent in the user space header is the number of list entries.) If there are no entries, then LOPtr is not changed, and the main program loop will terminate.
The first entry in the returned list is offset from the beginning of the user space by the number of bytes returned in field UspLstOfs in the user space header. Using the new pointer arithmetic, NxtJob adds UspLstOfs to pointer UspPtr and puts the result in LOPtr (Figure 11, Label G). This means that the field names in data structure LOLEntry can now be used.
NxtJob also calculates the end point of the list entries by multiplying the length of an entry (UspLstEntSz) by the number of entries (UspLst#Ent). This value is added to LOPtr and saved in LOEndPtr (Figure 11, Label H). The intent here is to never trespass beyond the bounds of known data. Incrementing your pointer beyond known data will often work, but what data you are looking at is undetermined. NxtJob then saves the job information to be used to find unique jobs and returns.
9. Process the first entry using names from the data structure. Each list entry is processed in the main loop by calling subroutines WriteRec and BldMsg. (This code is not shown.) Since LOPtr is now initialized, the names in the LOLEntry data structure can be used. WriteRec simply moves information from LOLEntry and writes a disk record. BldMsg formats information from LOLEntry into the message field, using several of the new built-in functions.
10. If there are more entries, add the entry length to the pointer. At the bottom of the main loop (Figure 10), NxtJob is called again to process additional list entries. This time, LOPtr is not null and is incremented to the next entry in the list by adding the length of a list entry, UspLstEntSz (Figure 11, label I).
As long as LOPtr is less than LOEndPtr, there are still list entries to process. NxtJob skips entries by incrementing LOPtr by the length of an entry until the next unique job is found (see Labels J and K of Figure 11).
If LOPtr is equal to (or greater than) LOEndPtr, there are no more entries and the last unique job was processed. LOPtr is set to null to indicate to the main loop that there are no more jobs, and also as a defensive programming strategy (see Labels L and M of Figure 11).
11. Process that entry and repeat until there are no more entries. The main loop goes back to the top and, while LOPtr isn’t null, processes each new job with subroutines WriteRec and BldMsg.
Once the main loop determines that LOPtr is null, it closes the output file and adds an ending to the message, again using some of the new built-in functions. (This code is not shown.) Then, it returns to the caller.
It’s Easy!
GETOBJUR is really quite a simple program. Other than a couple of pointers and using the Based keyword in the data structure definitions, there is little that most AS/400 developers haven’t seen. It moves down the list of entries by simply using EVAL to increment a pointer variable. No smoke, no mirrors, no unnecessary layers of abstraction. There is no practical upper limit on the number of list entries GETOBJUR, or other programs written this way, can handle.
This article touches only on using pointers to read data by incrementing a pointer. This type of use is by far the safest way to use pointers, and pointer arithmetic makes it easy.
There are other uses for pointers. You can also write data with pointers, and you can decrement pointers. If you want to, you can go as far to create linked lists, build and binary search dynamic arrays, and use other memory management techniques that until now have been practical only in C programs. But be careful! Set your pointer incorrectly and you can introduce subtle and hard-to-find bugs. (See the “Caveats on Pointer Arithmetic” sidebar.)
Don’t be afraid to use pointers. As demonstrated by GETOBJUR, they can simplify some tasks.
Caveats on Pointer Arithmetic
Know when to stop. If you are incrementing forward or backward through a list, always be sure that you know when you’ve hit the end of the data. If you are reading data, your program may crash if you exceed your boundary. Or, worse still, it may not crash, and you’ll introduce spurious information that may cause elusive bugs later. If you are writing and you exceed the bounds of your allotted area, you may crash, or you may be modifying data belonging to some other program in the stack. This may also be hard to find down the line.
As a defensive programming strategy, initialize each pointer to null and set it back to null when you are finished using it. This way, you’ll crash if you use it incorrectly, which is better than using or changing data that isn’t yours.
Pointer arithmetic increments or decrements by bytes. C, for example, increments a pointer by the size of the data type the pointer addresses.
You can subtract two pointers to get the byte difference between them.
Trying to add two pointers with an EVAL statement will cause a compile error, as will trying to multiply or divide a pointer. It is not specified how a pointer is internally represented, just as it isn’t specified how a date variable is internally represented. Adding pointers makes as much sense as adding dates. (What do you get if you add 1997-01-12 to 1998-12-31? Or if you multiply 1994-11-24 by 2? It doesn’t make sense, does it?) Don’t even think about trying to beat the compiler.
Dynamic Adjustment
The way IBM has structured the information returned by the list APIs is flexible. It allows IBM to add additional fields on the end of the header or list entry in new releases of the operating system. If you use the technique shown here, your program won’t falter when such a change is introduced. You don’t need to check your program, and you don’t need to recompile it.
No value added to a pointer is hardcoded in the program. Rather, at runtime, the values come from the data returned by the API, and the program automatically adjusts. Newly added fields are simply bypassed, and, as far as the program is concerned, they don’t exist. It didn’t need them before, and it doesn’t need them now.
An alternative, prepointer arithmetic technique uses a multiple occurrence data structure to map the list entries. This means that you have to hardcode the length of a list entry in your program and thus set the length at compile time. If a new version of the operating system starts returning a different length, your program may crash or may start providing garbage data. If you use this technique, for safety, you should review your code with each new operating system release.
Figure 1: A list of numbers that’s hard to interpret
Figure 2: A list of numbers that’s easier to interpret
 |
 |
 |
 |
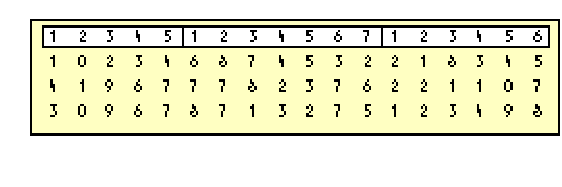 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |






















 More than ever, there is a demand for IT to deliver innovation. Your IBM i has been an essential part of your business operations for years. However, your organization may struggle to maintain the current system and implement new projects. The thousands of customers we've worked with and surveyed state that expectations regarding the digital footprint and vision of the company are not aligned with the current IT environment.
More than ever, there is a demand for IT to deliver innovation. Your IBM i has been an essential part of your business operations for years. However, your organization may struggle to maintain the current system and implement new projects. The thousands of customers we've worked with and surveyed state that expectations regarding the digital footprint and vision of the company are not aligned with the current IT environment. TRY the one package that solves all your document design and printing challenges on all your platforms. Produce bar code labels, electronic forms, ad hoc reports, and RFID tags – without programming! MarkMagic is the only document design and print solution that combines report writing, WYSIWYG label and forms design, and conditional printing in one integrated product. Make sure your data survives when catastrophe hits. Request your trial now! Request Now.
TRY the one package that solves all your document design and printing challenges on all your platforms. Produce bar code labels, electronic forms, ad hoc reports, and RFID tags – without programming! MarkMagic is the only document design and print solution that combines report writing, WYSIWYG label and forms design, and conditional printing in one integrated product. Make sure your data survives when catastrophe hits. Request your trial now! Request Now. Forms of ransomware has been around for over 30 years, and with more and more organizations suffering attacks each year, it continues to endure. What has made ransomware such a durable threat and what is the best way to combat it? In order to prevent ransomware, organizations must first understand how it works.
Forms of ransomware has been around for over 30 years, and with more and more organizations suffering attacks each year, it continues to endure. What has made ransomware such a durable threat and what is the best way to combat it? In order to prevent ransomware, organizations must first understand how it works. Disaster protection is vital to every business. Yet, it often consists of patched together procedures that are prone to error. From automatic backups to data encryption to media management, Robot automates the routine (yet often complex) tasks of iSeries backup and recovery, saving you time and money and making the process safer and more reliable. Automate your backups with the Robot Backup and Recovery Solution. Key features include:
Disaster protection is vital to every business. Yet, it often consists of patched together procedures that are prone to error. From automatic backups to data encryption to media management, Robot automates the routine (yet often complex) tasks of iSeries backup and recovery, saving you time and money and making the process safer and more reliable. Automate your backups with the Robot Backup and Recovery Solution. Key features include: Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online